
ANDE-RR
Jump to: Mission Objectives, Mission Instrumentation, Mission Parameters, Additional Information
Mission Photos:

Courtesy of NRL
Mission Objectives:
The Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment Risk Reduction (ANDERR) flight is a mission flown by the Naval Research Laboratory to monitor the thermospheric neutral density at an altitude of 350km. The primary mission objective is to test the deployment mechanism from the Space Shuttle for the ANDE flight in 2009. Scientific objectives of the ANDE risk reduction flight include:
- Verify deployment system.
- Monitor total neutral density along the orbit for improved orbit. determination of resident space objects.
- Monitor the spin rate and orientation of the spacecraft.
- Provide a test object for polarimetry studies using the HI-CLASS system at the Air Force Maui Optical and Supercomputing facility (AMOS).
The ANDERR mission consists of two spherical spacecraft fitted with retro-reflectors for satellite laser ranging (SLR), the Mock ANDE Active spacecraft (MAA) and the Fence Calibration spacecraft (FCal). Each spacecraft contains a small light-weight payload designed to determine the spin rate and orientation of the spacecraft from on-orbit measurements and from ground based observations. A unique design requirement of one satellite is to telemeter the data to the ground without external protrusions from the spherical spacecraft (i.e. an antenna).
On Dec. 25, 2007 the MAA (ANDERRA) spacecraft re-entered the atmosphere; the FCal (ANDERRP) spacecraft is re-entered on May 25, 2008.
The MAA satellite carried a communications system developed by the USNA that uses two aluminum hemispheres as the ends of a dipole antenna, at amateur radio frequencies. This system acted as a backup communications platform in the full ANDE mission, planned for 2009. The MAA also carried 6 photovoltaic cells that are positioned at the end points of three nearly orthogonal axes. These were used to determine spin vector orientation and spin rate. MAA also carried six onboard laser diode beacons (810 nm) that were commanded on during passes over AMOS, which observed the light from the diodes to deduce the MAA spin rate and orientation. A thermal monitoring system measured the temperature at several locations on the MAA spacecraft.
The Fcal satellite carried a communications system developed by the STENSAT group that uses a CubeSat as the bus for a communications system that operates at amateur radio frequencies. The FCal also carried 6 phototransistors that were positioned at the end points of three nearly orthogonal axes. These were used to determine spin vector orientation and spin rate. A thermal monitoring system measured the temperature at several locations on the FCal spacecraft.
 |
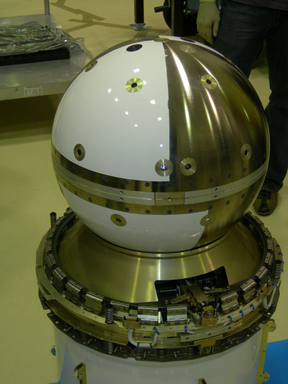 |
MAA Spacecraft: 19” diameter, 52.04 kg. |
FCal Spacecraft: 17.5” diameter, 62.70 kg |
ANDE has the following on-board instrumentation and components:
- Active Sphere:
- Modulating Retro-Reflector (MRR) Array
- Final layout analysis in progress
- One hemisphere densely populated
- One hemisphere with single MRR
- Final layout analysis in progress
- Thermal Control System (± 5 C)
- Thermal Monitoring System (TMS) ( ≤ 1C)
- Global Positioning Sensor (GPS)
- Wind and Temperature Spectrometer (WATS) (1-46 amu)
- Backup Communications System
- Photovoltaic Arrays
- Lithium Ion Batteries
- Modulating Retro-Reflector (MRR) Array
- Passive Sphere:
- Retro-Reflector Array
Mission Parameters:
| ANDE-RR Active (MAA) | ANDE-RR Passive (FCal) | |
| Sponsor: | NRL | NRL |
| Expected Life: | 1-3 years | 1 year |
| Primary Applications: | determine total atmospheric density in orbital plane | determine total atmospheric density in orbital plane |
| Primary SLR Applications: | Precision orbit determination | Precision orbit determination |
| COSPAR ID: | 0605506 | 0605510 |
| SIC Code: | 1071 | 1072 |
| Satellite Catalog (NORAD) Number: | 29664 | 29667 |
| Launch Date: | December 21, 2006 | December 21, 2006 |
| RRA Diameter: | 12.7 mm | 12.7 mm |
| RRA Shape: | sphere | sphere |
| Reflectors: | 30 corner cubes | 30 corner cubes |
| Orbit: | circular, non sun-synchronous | circular, non sun-synchronous |
| Shape: | 19.0 inch diameter sphere | 17.5 inch diameter sphere |
| Inclination: | 51.6 degrees | 51.6 degrees |
| Eccentricity: | 0.0007 | 0.0007 |
| Altitude: | ~400 km | ~400 km |
| Weight: | 52.04 kg | 62.70 kg |
Additional Information:
Web sites:
- NASA
- NASA Space Station Expedition 14 overview
- USNO
- Mass-Spectrometer-Incoherent-Scatter (MSIS) model (NRL)
Publications:
- Nicholas, A.C., Picone, J.M., Emmert, J., DeYoung, J., Healy, L., Wasiczko, L., Davis, M., Cox, C., “Preliminary Results from the Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment Risk Reduction Mission”, Proc. of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, paper #AAS 07-265, Mackinac Island, MI, Aug 20-24, 2007
- Nicholas, A.C., et al. "ANDE Risk Reduction Flight"
- Nicholas, A.C., Finne, T., Davis, M.A., "Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment Risk Reduction (ANDE-RR) Flight Hardware Details"




